What is MFI (Mean or Median Fluorescence Intensity) and how do I calculate it in FCS Express?
What is MFI?
The term, MFI, is used commonly within the flow cytometry community. However, it does not have a universal meaning, and it is incumbent upon the researcher or scientist to define it.
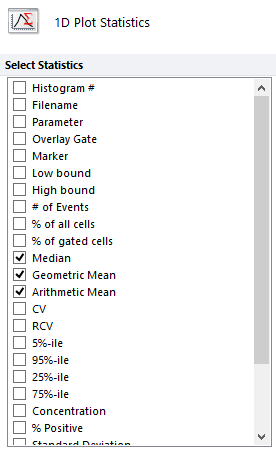
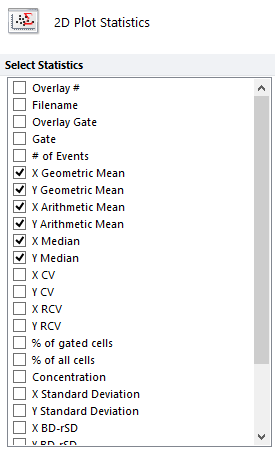
MFI refers to the Mean, or Median, Fluorescence Intensity. In FCS Express, you may select three statistics to represent MFI for your data.
- Arithmetic mean, or Average, is the sum of N numbers divided by N.
- Geometric mean is the Nth root of the product of N numbers.
- Median, which is the 50th percentile of a population, represents the value at which half of a measured population is above and the other half below.
Using Statistics in FCS Express to report MFI
Once you have determined the appropriate statistic for MFI in your study, you can insert a statistics table to display the statistics of interest. Simply right-click on a plot and choose the appropriate option to insert either Histogram Statistics, Gate Statistics, or Quadrant Statistics. Additionally, integrated spreadsheets may be used to report MFI values.
For univariate (1D) plots, such as histograms, you can choose to display either the Arithmetic Mean, the Geometric Mean, or the Median, for the X-axis parameter.
For bivariate (2D) plots, you can select X Geometric Mean, Y Geometric Mean, X Arithmetic Mean, Y Arithmetic Mean, X Median, and Y Median, where X and Y represent the X and Y parameters that are being displayed in the 2D plot of interest.
These statistical tables can be formatted rather easily, by right-clicking on the table and choosing the statistics of interest, or, by formatting the table.
Spreadsheets and tokens can also be inserted in the analysis to quickly show a statistic of interest.
Tokens are dynamic text that updates in real-time. Tokens can be inserted in text boxes within an FCS Express analysis, or placed within a spreadsheet, and can represent a statistic, keyword, or properties of the layout, among other bits of information regarding the analysis.
Cautions
- While the Mean might be most useful when used to describe normal distributions and not bi-modal or multi-modal data, the Median is a non-parametric statistic in that it is a robust indicator of the central tendency of your data, regardless of the underlying data distribution.
- The Arithmetic Mean is affected by outliers, while the Median is less sensitive to outliers.
- In general, the geometric mean statistic is only useful for positive values.
- This especially applies to digital FCS 3.x flow cytometry data.
- If a population contains any events that have a negative raw value, FCS Express will display the geometric mean for that population:
- as N/A in a statistics table,
- or as ##ERROR## when a token is used to represent that statistic.

- Scaling choices will impact how the data is presented visually on the plot, but will not affect the statistical value.
Additional Reading
-
Installation
-
Licenses
-
- Can I get more information regarding the Add-Ons that can be purchased with a license?
- Can I lock my template based on an electronic signature?
- Does FCS Express have any features to help meet 21 CFR Part 11 compliance?
- Does FCS Express have Quality Control features?
- Does FCS Express offer Single Sign On capability?
- How do I configure SQL Server to host a database for FCS Express?
- What database options are available when I purchase the Security option?
- What is the difference between the different types of Users that are available with a Security and Logging license?
- What is the difference between the Logging option and System Level Audit Trails?
- What SQL Server permissions are needed?
-
-
- Can I share my USB dongle or countercode license with another user?
- Can I track usage of the internet dongle?
- Can I try out the Internet Dongle before I make a purchase?
- Can the administrator log users out?
- Do you have to be connected to the internet at all times with the Internet dongle?
- How can users be added to an internet dongle license?
- How do I activate my dongle?
- How do I change my internet dongle/site license password?
- How many people can be logged in at the same time?
- How many user accounts can I create?
- If a user left the computer running can the user log themselves out from another computer?
- What are the differences between the internet dongle and network licensing options?
- What happens if I lose my internet connection?
- What happens if the user leaves the computer without logging out?
- What happens to the users login in case of an unexpected interruption? For instance, a software crash, power failure, etc.
- Why am I receiving a message that FCS Express cannot connect to De Novo Software servers?
- Show all articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
- Can I convert my Cytek license from the countercode licensing option to another licensing option?
- How can I claim my license purchased through BD Accuri Cytometers?
- How can I claim my license purchased through BD Biosciences?
- How can I claim my license purchased through Nexcelom Biosciences?
- How can I claim my license purchased through Sysmex-Partec GmbH?
- How can I claim the FCS Express license that came with my Cytek instrument purchase?
-
-
Layouts & Loading Data
-
- Are Beckman Coulter LMD files unique?
- Can I find a support resource page for the analysis of Cytek data in FCS Express?
- How can I easily create the "filename" column in the "ExtraKeywordsTable.csv" file?
- How can I load a Sony MA900 Index Sort file into FCS Express?
- How can I load data from the BD Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer?
- How can I load MACSQuantify files that were exported from MACSQuantify software version 3.0.1?
- How can I quickly reload all of the data files in the data list?
- How do I change the display in my plots from one data file to another data file?
- How do I export .ICE files from Thermo Cellomics HCS Studio?
- How do I tell FCS Express what plate size to use if that information is not included in the data file?
- How do I upload files to the De Novo Software FTP site?
- How do I use BD Accuri CFlow files with Multicycle DNA analysis in FCS Express?
- How do I work with images from the Thermo Scientific Attune CytPix?
- What is the Elapsed Time setting in the Gallios software and how do I convert it to real time?
- Why am I seeing a warning message when loading my Cytek data onto a layout object?
- Why are iterations in my Data List gray?
- Why are there sometimes access violations when I save and load files?
- Why do I get the message that a data file exported from a FACSDiva™ Experiment is invalid?
- Show all articles ( 3 ) Collapse Articles
-
- How are existing quadrants handled when an old layout is opened in version 7.20 and later?
- How can I set quadrants to behave like conventional gates?
- How can I set quadrants to behave like in earlier versions?
- Quadrants in FCS Express versions 7.20 / 7.24 and later
- Why does the Quadrants Options window appear when I open an older layout in version 7.24?
- Why have percentages reported by quadrants changed after updating to FCS Express version 7.20.20?
-
Data Analysis
-
- Caveats when using Biexponential Scaling with automatic Below Zero parameter detection in the presence of outliers.
- How can I create a merged data with equally-sized downsampled samples?
- How can I do pre-processing for high-dimensional data analysis?
- How can I explore tSNE/UMAP plots?
- How do I use SPADE?
- What is FlowSOM?
- What is T-SNE?
- What is UMAP?
-
- Can FCS Express integrate Python scripts?
- Can I use the FlowAI script in FCS Express?
- Can I use the FlowClean R Script with FCS Express?
- How can I create a matrix of autofluorescence, and import autofluorescence into EasyPanel?
- How can I recreate ratiometric data acquired in FACSDiva?
- How do I use R Integration with FCS Express?
- How does FCS Express implement software compensation?
- If my data does not have a Time parameter, can I create one?
- What is compensation?
- What is the compensation workflow in FCS Express?
- When acquiring spectral data, should my single-stained controls be "as bright or brighter" than my fully-stained sample?
-
- Can a set of quadrants be both percentile and floating?
- Can I customize the display of my data from different instruments?
- Can I disable the live updating feature?
- How can I display all of my detectors for my Cytek data?
- How can I set FCS Express so my FCS 3.0 biexponential data looks the same as it did in the BD FACSDiva software?
- How do I display Summit data in FCS Express as it appears in the Summit Software?
- How do I fix the biexponential axes on a plot?
- How do I rescale CytoFLEX data so it displays as it did at acquisition?
- How do I update my density and contour plots created in Version 4 to use the newest color palette?
- What are resolution options?
- What is Biexponential and Hyperlog Scaling?
- What is the best way to set FCS Express to display FCS 3.0 data from FACSDiva on a 4 decade log scale?
- Where can I get more information regarding DNA analysis using the Multicycle AV?
- Why can’t I change my plot axis labels from the Name keyword to the Stain keyword?
- Why do I see a warning message when inserting a Spectrum Plot?
- Why do my dot plots appear sparse and blocky?
- Why is the text on the right most label cut off my plot?
- Show all articles ( 2 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Can I create an output file that contains the same plot from each data file on a single page?
- How can I export my spectral data files from FCS Express with unmixing applied?
- How can I successfully export a GatingML file?
- How do the batch processing run modes differ, and why would I use them?
- Why do I get an “Old format or invalid type library” error when using Microsoft excel during batch analysis?
-
- How are statistics in FCS Express calculated compared to how they are calculated in BD FACSDiva?
- How can I display my statistical data in Scientific Notation?
- How do I calculate EC/IC Anything?
- What is “Stain Index” and how do I calculate it with FCS Express?
- What is MFI (Mean or Median Fluorescence Intensity) and how do I calculate it in FCS Express?
- Why have percentages reported by quadrants changed after updating to FCS Express version 7.20.20?
- Why is the Geometric Mean being reported as NaN or ##ERROR##?
-
-
Image Cytometry
-
- How do I adjust the axes to display small particle data from Amnis CellStream?
- How do I choose which images and parameters to view in a Data Grid?
- How do I export/save data from IDEAS software and load it in FCS Express?
- How do I make my images in the data grid larger?
- How do I pseudo-color images in a data grid?
- How do I work with Amnis derived image cytometry data in FCS Express?
-
- Can I display heat maps with my Image Cytometry data?
- Can I work with data from PerkinElmer Instruments?
- Do you offer 21 CFR Part 11 compliance options for the Image Cytometry Version?
- Do you offer image segmentation or image analysis?
- How can Attune™ CytPix data sets with images (.ACS files) be merged for high dimensional analysis?
- How do I use CellProfiler Data with FCS Express?
- How do I use ImageJ with FCS Express?
- What file formats are compatible with FCS Express Image Cytometry?
- Where can I find Nexcelom Resources and Applications?
-
-
FCS Express on Mac
-
Upgrading FCS Express
-
- Can different versions of FCS Express exist on the same computer?
- How can I view and convert my V3 layouts to FCS Express 7?
- How do I import my version 3 security databases into newer versions of FCS Express?
- How do I update Density Plots created in Version 4?
- Is there an upgrade discount from earlier versions of FCS Express?
- Version 4 Internet Dongle Retirement
- Why are my density plots from V3 not displayed correctly in later versions?
- Why are there fewer outlier dots on my FCS Express 5 and later density plots than in V4?
-
Clinical & Validation Ready
-
- Can I get more information regarding the Add-Ons that can be purchased with a license?
- Can I lock my template based on an electronic signature?
- Does FCS Express have any features to help meet 21 CFR Part 11 compliance?
- What is the difference between the different types of Users that are available with a Security and Logging license?
- What is the difference between the Logging option and System Level Audit Trails?

